The Duravant family of operating companies serve the food processing, packaging and material handling segments.
What is Plastic Injection Mold and How Does It Work?
Plastic Injection Mold is a key technology in manufacturing. It allows companies to create complex shapes efficiently. This process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold. The mold is then cooled, forming the desired product.
Understanding how a Plastic Injection Mold works is fascinating. It combines engineering precision with artistic design. Each mold reflects the creativity and intent of its designer. However, creating a perfect mold can be challenging. Small errors can lead to significant defects in the final product.
The versatility of Plastic Injection Molds is remarkable. They can be used for everything from small components to larger items. Despite its advantages, the process requires careful planning. Mistakes can happen during the design or production phases. Reflecting on these challenges helps improve future projects.
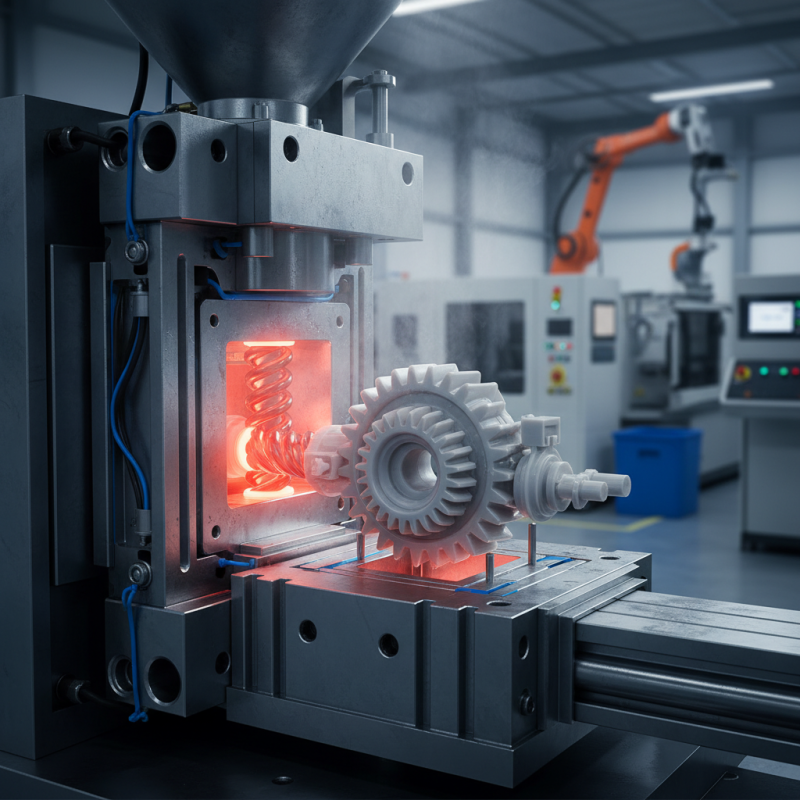
What is Plastic Injection Mold?
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It produces parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold. The process is valuable in various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical fields. According to industry reports, the global market for plastic injection molding is expected to reach $300 billion by 2025, highlighting its importance.
The process begins with heating plastic pellets until they become liquid. This liquid is then forced into a mold—typically made from steel or aluminum. A 2019 report noted that about 90% of plastic products produced globally utilize this method. After cooling, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. However, this method does come with challenges. Ensuring precise control over temperature and pressure can be difficult. Variations can lead to defects in the final product.
Moreover, the environmental impact is a growing concern. While plastic injection molding is efficient, it contributes to plastic waste. Industry experts suggest that over 30% of injected parts may end up as scrap. This statistic raises questions about sustainability and innovation in the field. Balancing efficiency with eco-friendliness remains an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
The Components of a Plastic Injection Mold
Plastic injection molds are intricate tools used in the manufacturing process. They consist of several critical components. Each part plays a vital role in producing high-quality plastic items. Understanding these components helps in grasping how the molds function.
Temperature control systems are essential for managing the cooling phase. They help in achieving the right solidification of the plastic. Without proper cooling, products may warp. It’s interesting that even experienced mold makers occasionally face challenges in maintaining ideal temperatures. Each component, though well-designed, demands careful attention during production. Small variations can lead to significant issues. Understanding and refining these components is crucial for achieving better results.
How the Injection Molding Process Works
The injection molding process is a highly efficient way to produce plastic parts. It starts with melting plastic pellets. The raw material is heated to a specific temperature, transforming it into a viscous liquid. Reports indicate that about 20% of the overall time is spent heating and mixing the plastic. Precision is crucial.
A significant step involves injecting this molten plastic into a mold. Molds can be complex, featuring detailed designs that define the final product. It typically takes mere seconds for the injection to occur. Once filled, cooling begins. The cooling stage is critical, as it accounts for about 60% of the total cycle time. Wait times can vary. Parts may warp if cooled too quickly.
Not all molds perform perfectly. Variations in temperature or pressure can lead to defects. Industry studies suggest that 3-5% of produced items may not meet quality standards. Constant monitoring is necessary to reduce waste. Molding techniques evolve with technology. Future developments focus on improving efficiency and lowering costs. However, challenges remain as manufacturers strive for greater perfection.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is widely used across various industries. The automotive sector, for instance, relies heavily on this process. Reports indicate that over 30% of plastic parts in vehicles are produced through injection molding. This method allows for the production of complex shapes and robust components, essential for modern designs.
Another significant application is in consumer goods. In fact, around 40% of plastic products, such as household items and electronic casings, are manufactured using this technique. The flexibility of injection molding accommodates different materials and colors, catering to customer preferences. However, it is crucial to ensure quality control throughout the production process to avoid defects and waste.
Healthcare is also embracing plastic injection molding. Surgical instruments and medical devices often require precision parts made from high-quality plastics. Research suggests that nearly 25% of medical applications utilize this technology. While the benefits are clear, there is a growing challenge in managing the environmental impact of plastic waste generated from production. Finding sustainable practices and materials remains a top priority for the industry.
Benefits and Challenges of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process, offering several benefits. One major advantage is efficiency. This method allows for mass production of parts. Many identical pieces can be made in a short time. The process also minimizes waste. The material usage is optimized, which saves costs.
However, plastic injection molding comes with its challenges. The initial setup cost can be high. Producing molds requires significant investment. This can deter smaller companies from using the method. Additionally, design flaws may arise during production. Adjustments to the mold can be time-consuming. These factors can lead to increased lead times.
Another issue is environmental impact. While the process is efficient, it heavily relies on plastics. Some materials may not be recyclable. This raises concerns about sustainability. Companies must navigate these challenges to balance efficiency and eco-friendliness. There is also a need for continuous improvement in design and production techniques. Addressing these issues could lead to a more responsible approach to plastic injection molding.











